Zoom AI Performance Report 2025

Over the past year, AI capabilities within communication platforms have advanced significantly, delivering more accurate, reliable, and context-aware transcription, translation, and real-time assistance. These developments enable users to interact more effectively in meetings, collaborate across languages, and maintain clearer records of discussions, ultimately supporting better decision-making and productivity.
This report presents an evaluation we commissioned of real-time transcription, closed captions, and translation performance for English, Spanish, French, and Japanese across multiple platforms. Evaluated providers include:
- Google Meet
- Microsoft Teams
- Otter.ai
- Zoom Workplace
The assessment focuses on multiple metrics, including word-level accuracy, rare word recognition, orthographic correctness, speaker labeling, closed caption stability, and translation quality.
About TestDevLab
TestDevLab (TDL) offers software testing & quality assurance services for mobile, web, and desktop applications and custom testing tool development. They specialize in software testing and quality assurance, developing advanced custom solutions for security, battery, and data usage testing of mobile apps. They also offer video and audio quality assessment for VoIP or communications apps and products for automated backend API, as well as web load and performance testing.
TestDevLab team comprises 500+ highly experienced engineers who focus on software testing and development. The majority of their test engineers hold International Software Testing Qualifications Board (ISTQB) certifications, offering a high level of expertise in software testing according to industry standards and service quality.
The testing covered a diverse range of real-world meeting scenarios designed to evaluate AI-supported features across communication platforms. These scenarios included small meetings with two to three participants and larger panels of up to fourteen participants. Meetings spanned various contexts, from technical discussions and project management calls to podcasts, conferences, and casual conversations, incorporating accents, background noise, overlapping speech, and reverb.
For meeting summaries, the default platform settings were used for all providers. On Zoom, this means the federated approach was applied, which may leverage multiple underlying AI models rather than a single in-house model. Each test scenario was conducted five times to mitigate variability that can occur in a single call.
During testing, participants were divided into speakers and listeners, with one listener serving as the host who initiated the online call and enabled transcription. Audio playback for each participant was segmented and played from separate user accounts to simulate an actual multi-participant call, providing consistent conditions and helping prevent skewed results. Multiple languages were included for closed captions, with participants monitoring and recording the captions in real time across English, French, Japanese, and Spanish. Otter.ai, which operates as a third-party transcription tool connected to Zoom, was included in the testing, although it was not involved in Closed Captions scenarios due to its design.
Captured Metrics
The study captured a comprehensive set of metrics to evaluate the performance of AI-supported features in communication platforms. These metrics included:
- Meeting Summary: Overall evaluation, conciseness, clarity, relevance, accuracy, hallucinations, completeness, objectivity, clarity of action items, context, structure, and entity recognition (identifying key people, organizations, dates, and other important details).
- Transcription (ASR) & Closed Captions (CC): Word error rates (Normalized WER and Rare WER) and speaker label accuracy.
- Closed Captions Translation: Translation quality measured via MetricX and COMET.
- Closed Captions Flickering: Unstable Partial Word Ratio (UPWR) and Unstable Partial Segment Ratio (UPSR), including total segment variants.
Each metric was interpreted according to best practices, with higher percentages indicating better performance for certain metrics and lower values indicating better performance for others, such as word error rates and flickering ratios.
Hardware and App Versions
Testing was conducted across multiple devices and applications, with all participants using virtual audio routing to ensure consistency and remove interference from physical microphones. All tests were run on a MacBook Pro M1 (2020) running macOS Sequoia 15.4.1. Software details included:
| Provider / Tool | App Version |
| Zoom | 6.4.6 (53970) |
| Microsoft Teams | 25093.2105.3614.8220 |
| Google Meet | Chrome 136.0.7103.94 |
| Otter.ai | Chrome 136.0.7103.94 |
Additional shared settings included muting all listeners, disabling cameras, and using a virtual two-channel audio device to inject audio directly into the system. Audio output for speakers remained on the device to maintain consistent playback across applications.
Across the scenarios tested, Zoom consistently demonstrated strong performance in transcription, closed captions, translation, and meeting summaries. While all providers showed strengths in certain areas, three scenarios highlighted Zoom’s relative advantages:
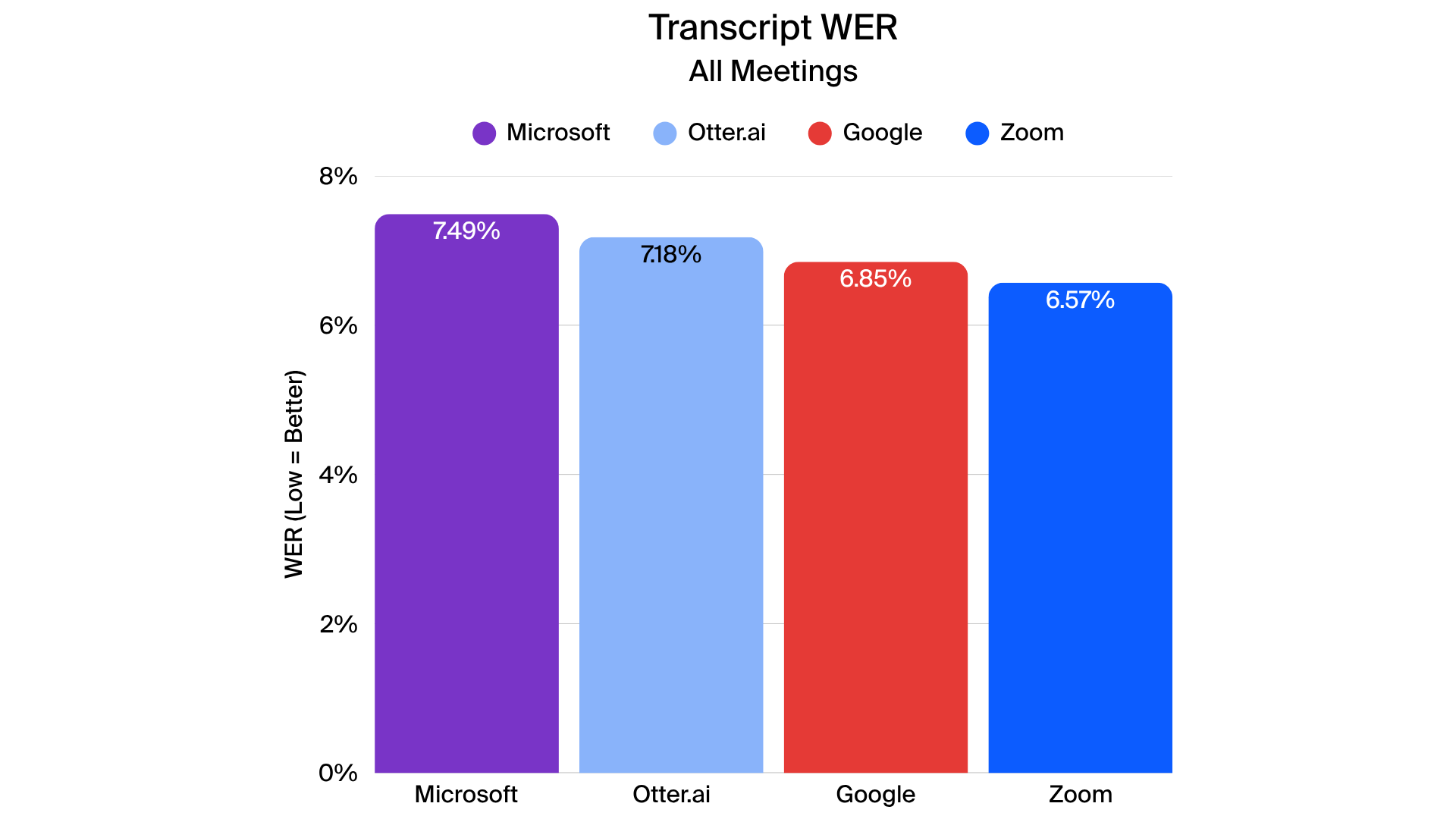
- Lowest error rates in transcription
- Zoom achieved the best word error rates (WER) score across real meeting scenarios.
- Detection of rare words surpassed other major providers, demonstrating higher transcription fidelity.
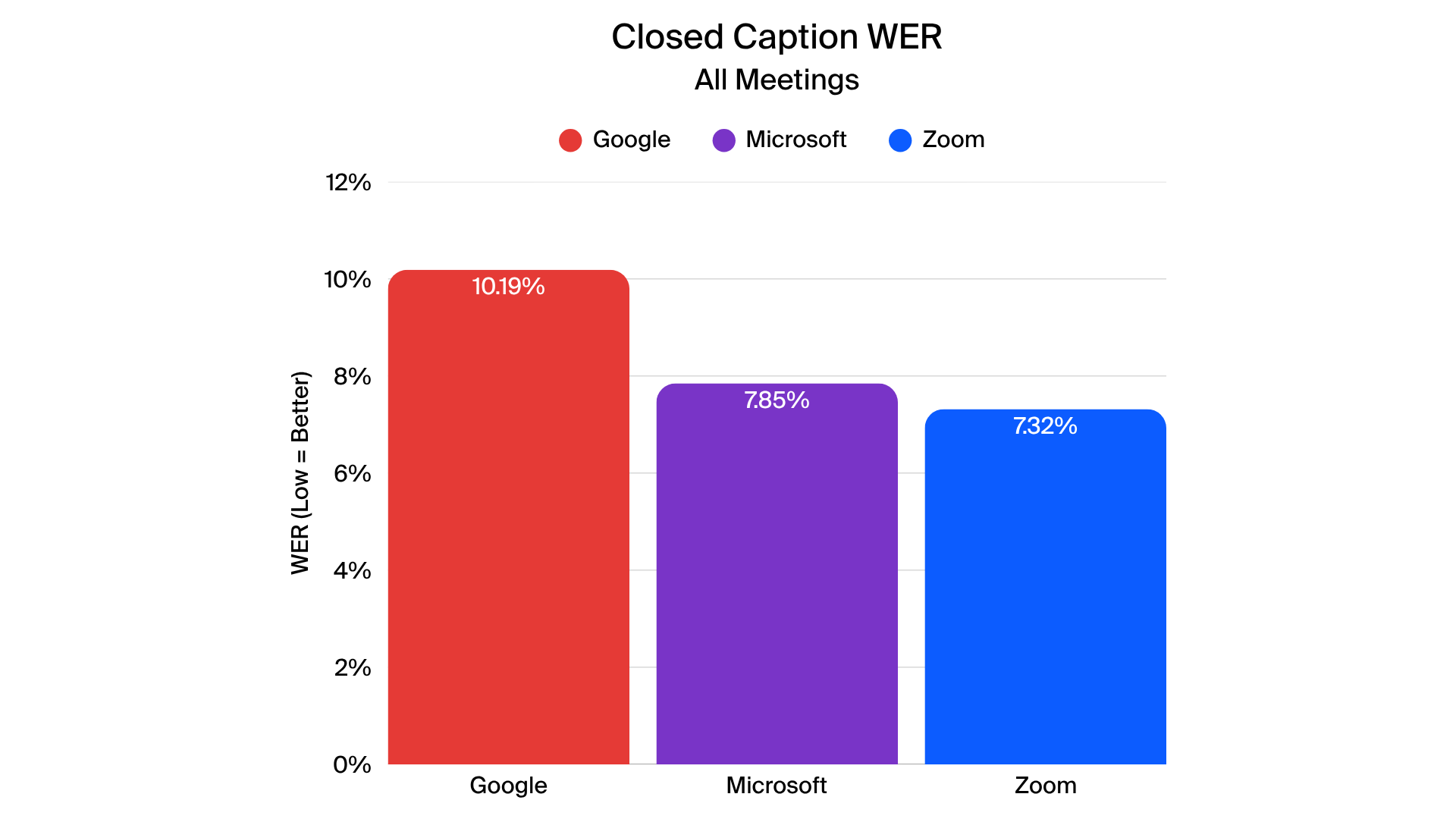
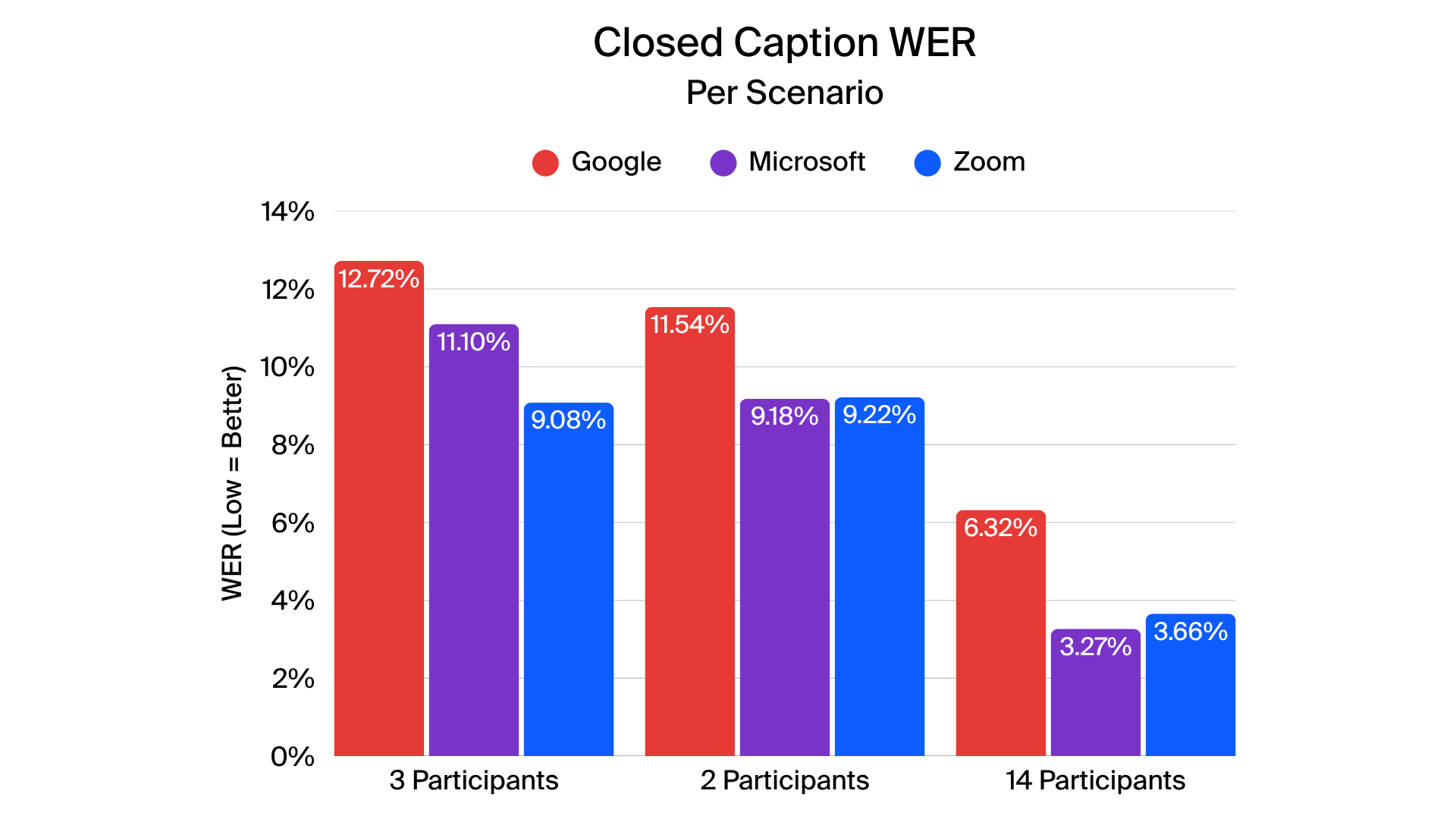
- Accurate and stable closed captions
- Zoom had the best WER and RWER scores in real meeting scenarios, producing clearer captions.
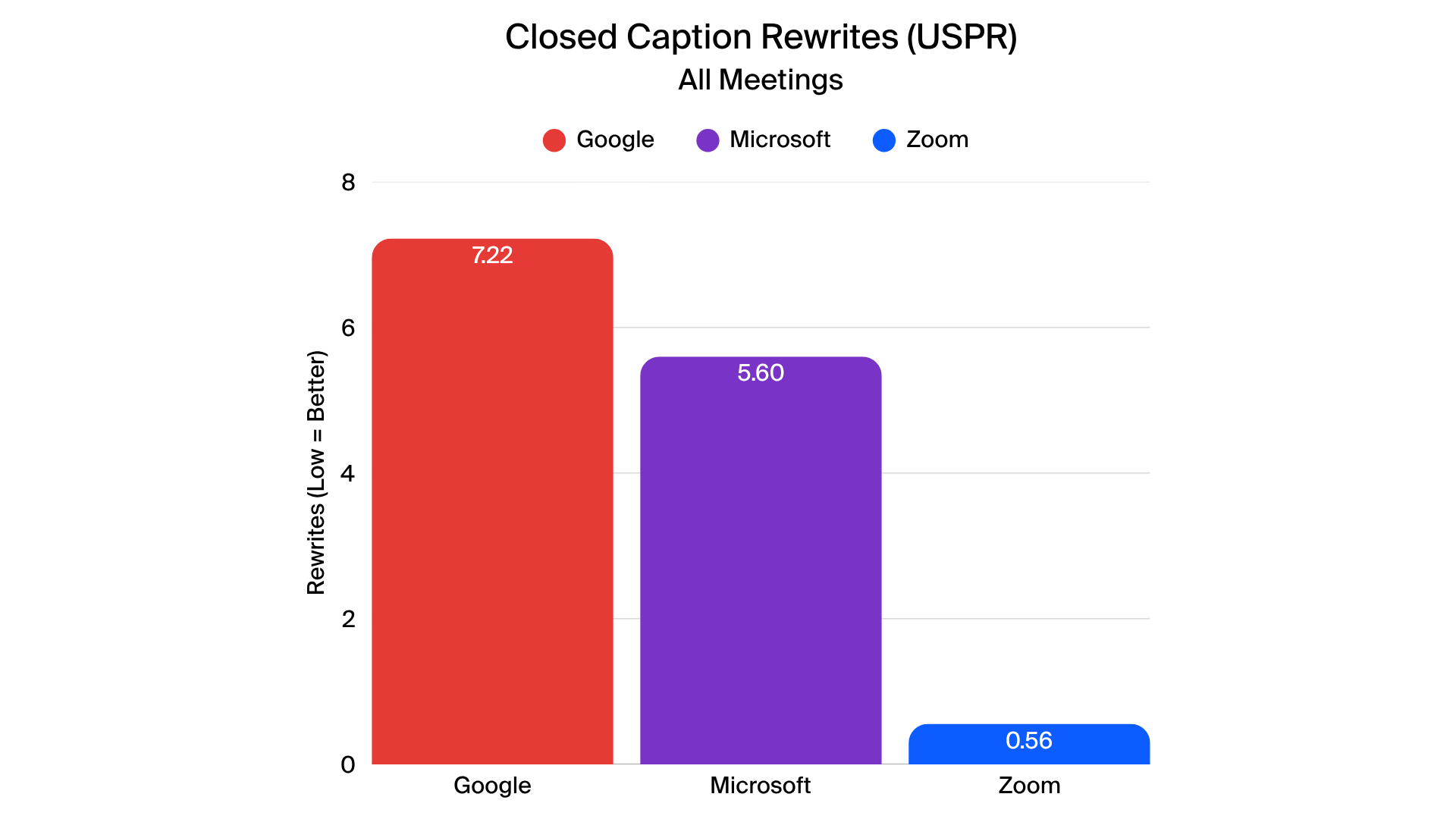
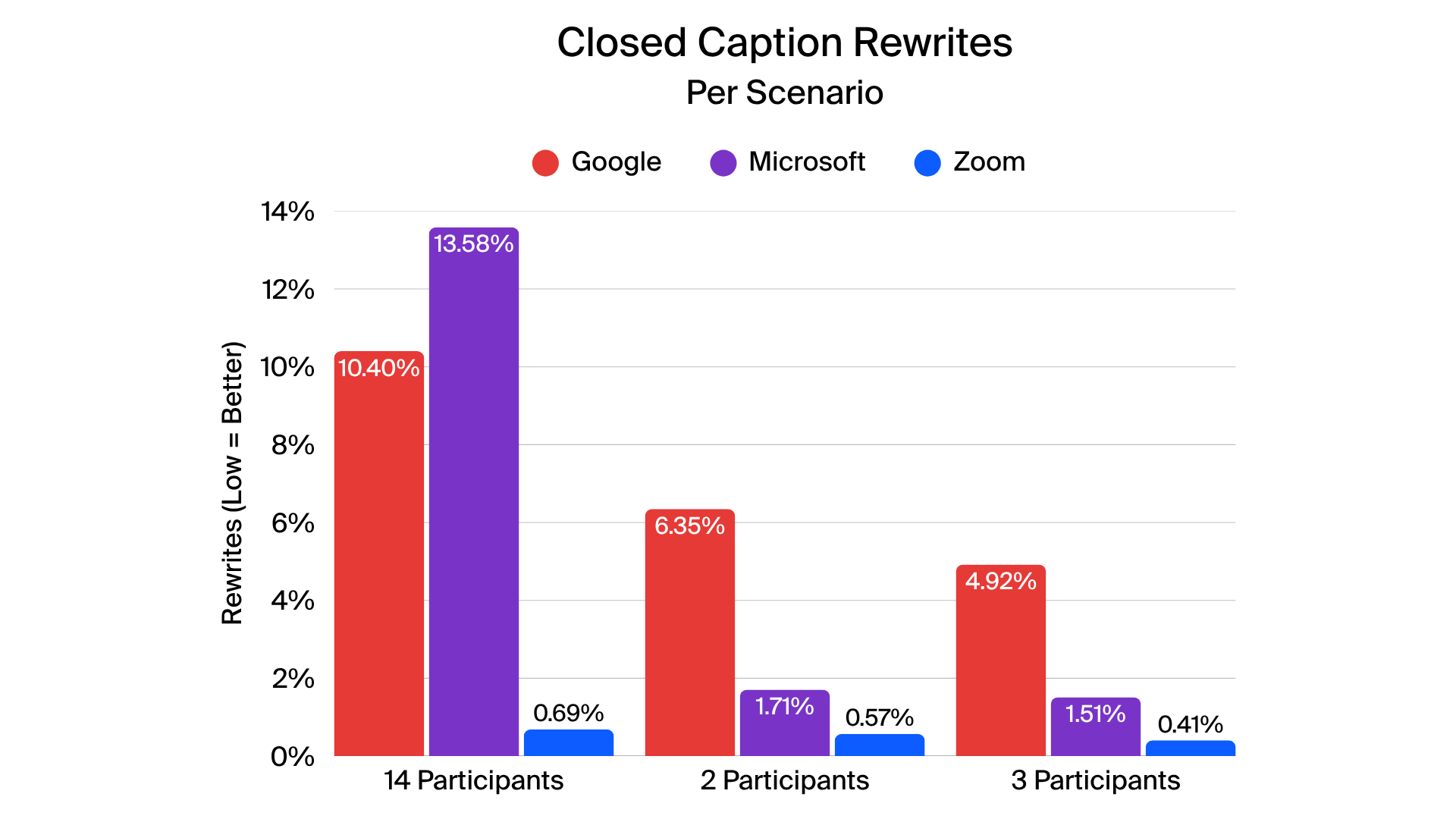
- Closed captions required fewer rewrites, providing a more comprehensive and readable experience for participants.
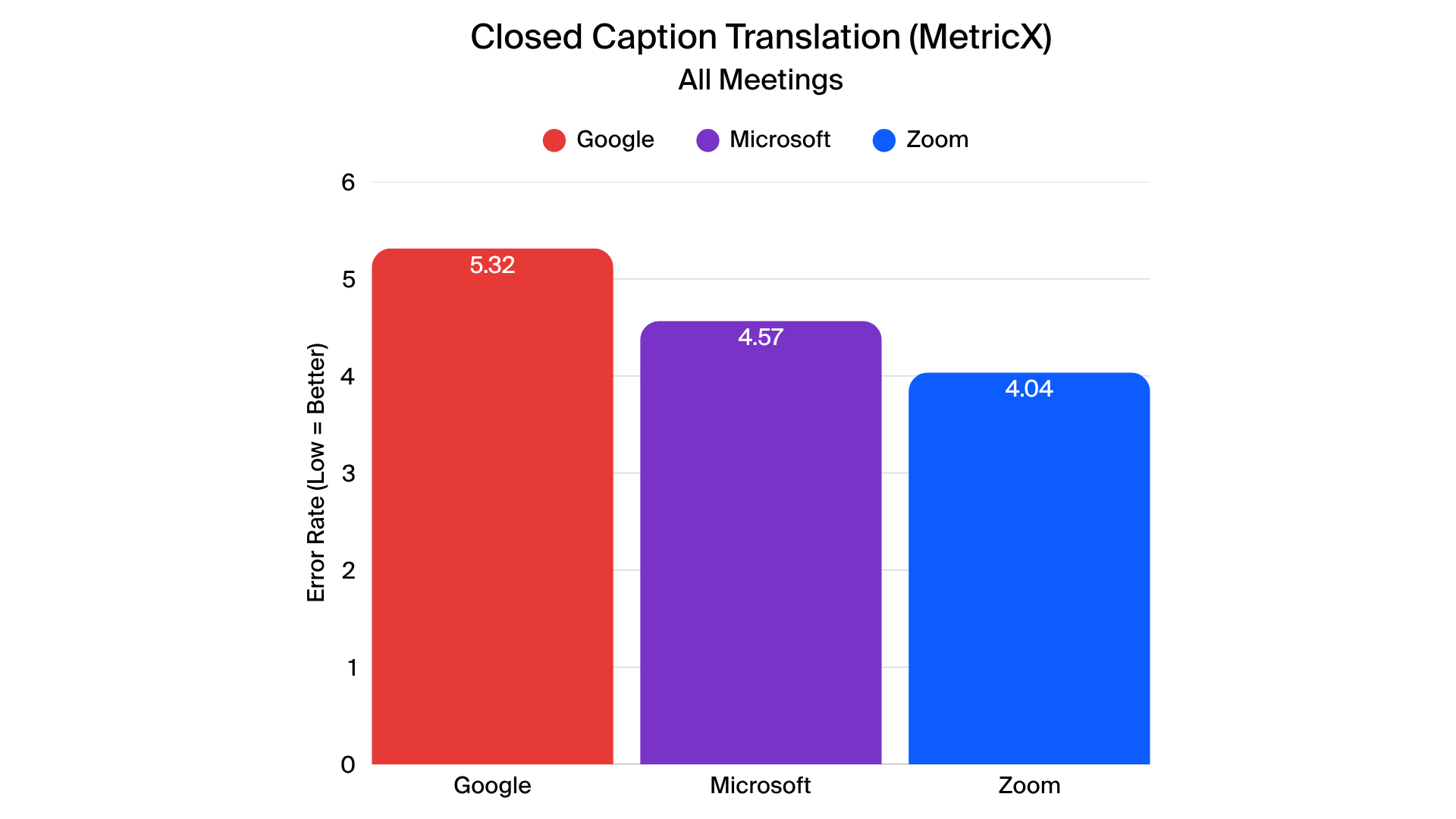
- Effective translated captions
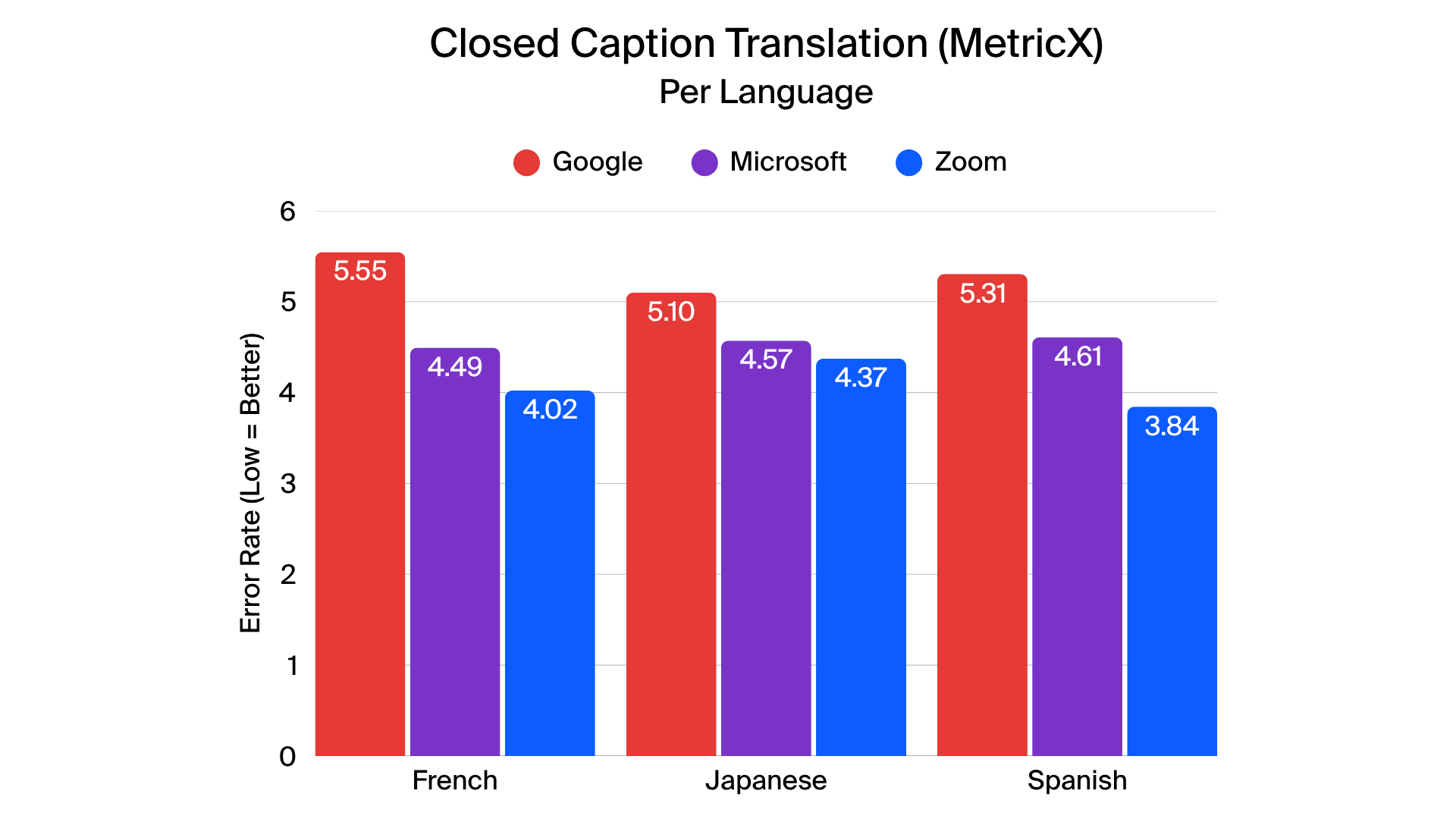
- Zoom led in translation quality for English-to-French, English-to-Spanish, and English-to-Japanese closed captions.
- Evaluation metrics reflected accurate context, grammar, and terminology across languages, providing clear and reliable translated captions.
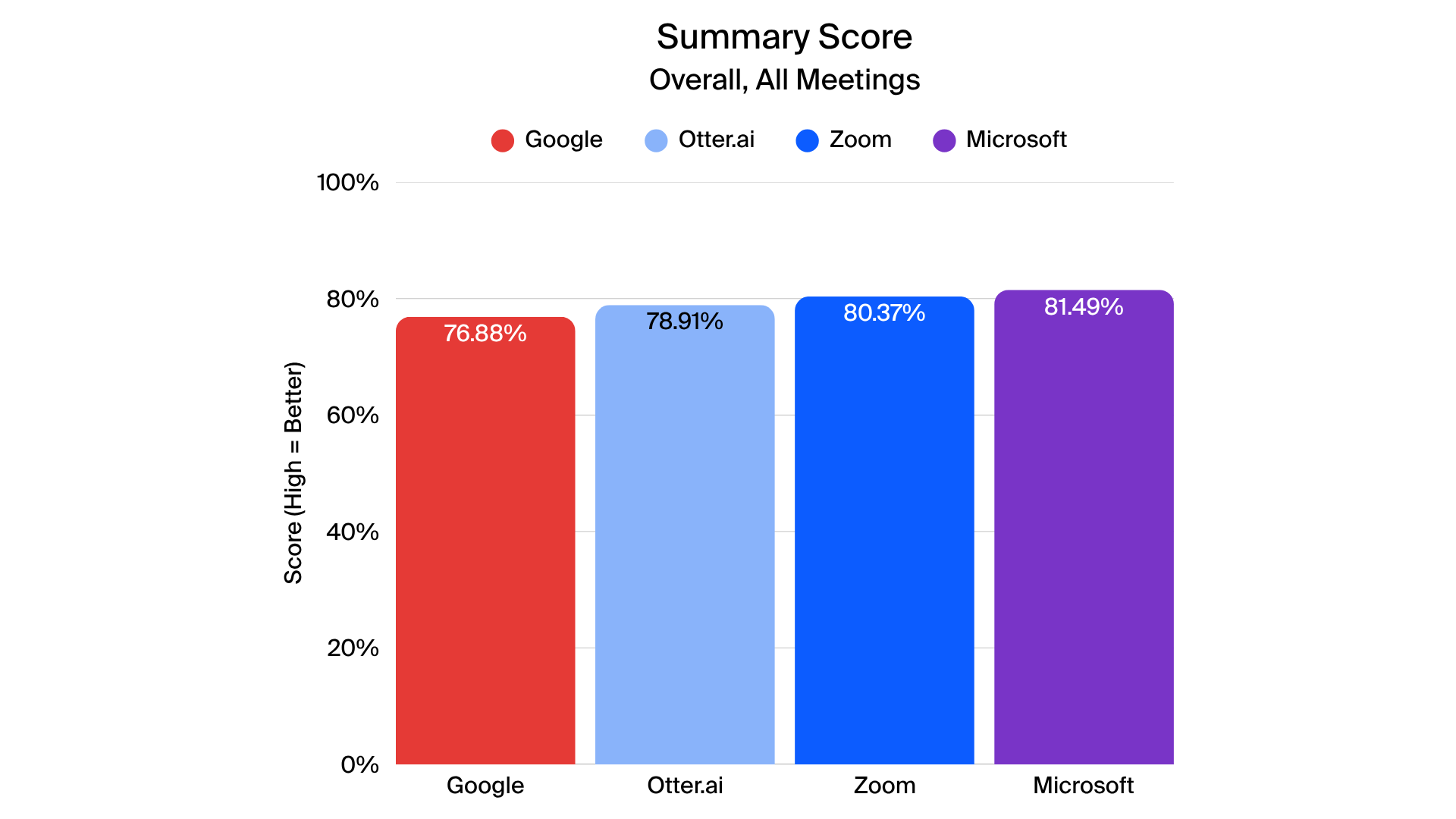
- Concise meeting summaries
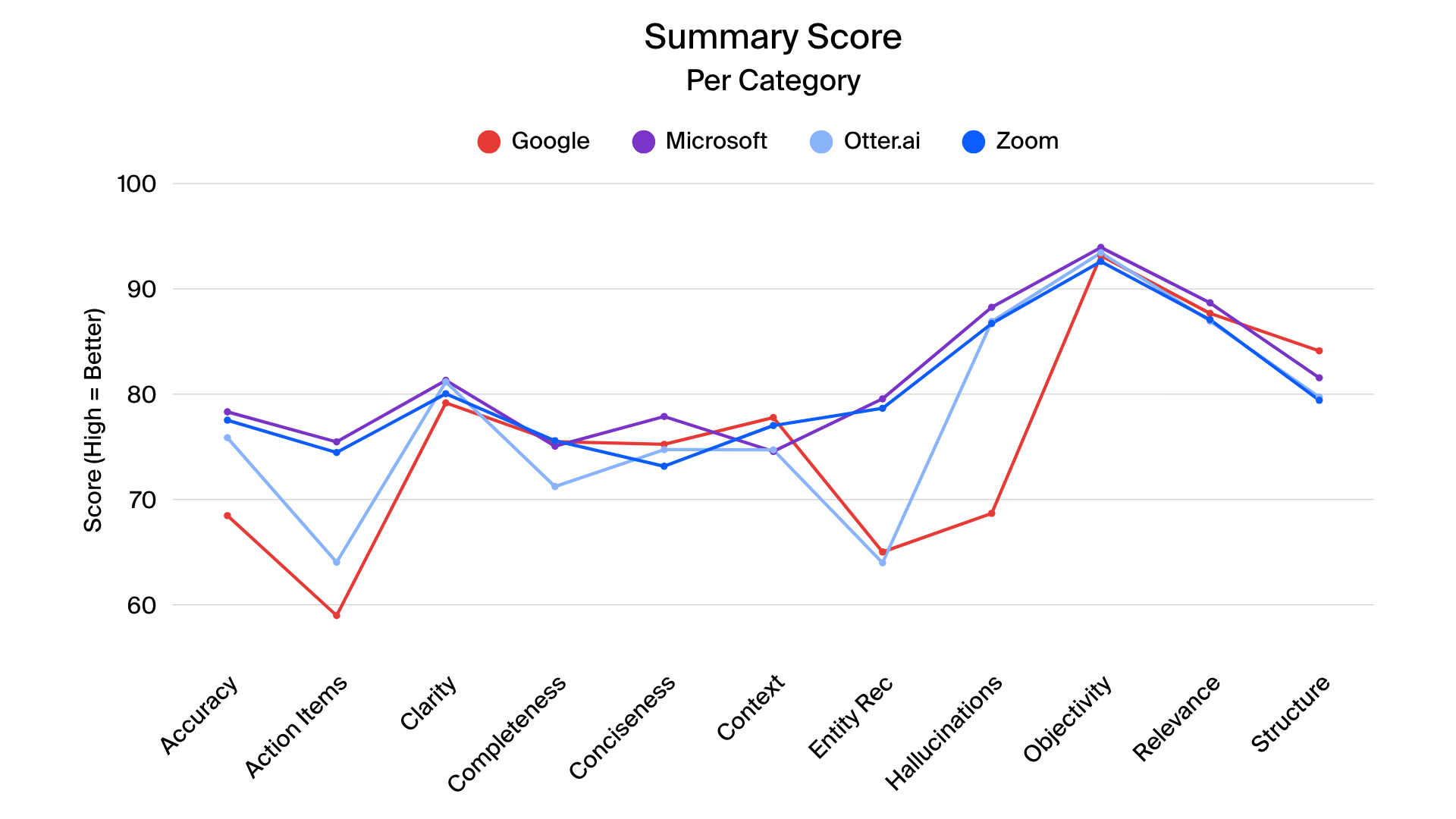
- Zoom’s meeting summaries were highly concise, approaching Microsoft’s quality and outperforming Google and Otter.ai in action item detection and entity recognition.
- The summaries effectively captured key points, reduced hallucinations, and highlighted relevant action items.
The detailed results expand on the high-level findings, offering insight into each provider’s performance across transcription, closed captions, translated captions, and meeting summaries. While all providers demonstrated strengths in specific areas, notable trends emerged when examining scenario-specific metrics.
Transcription (ASR)
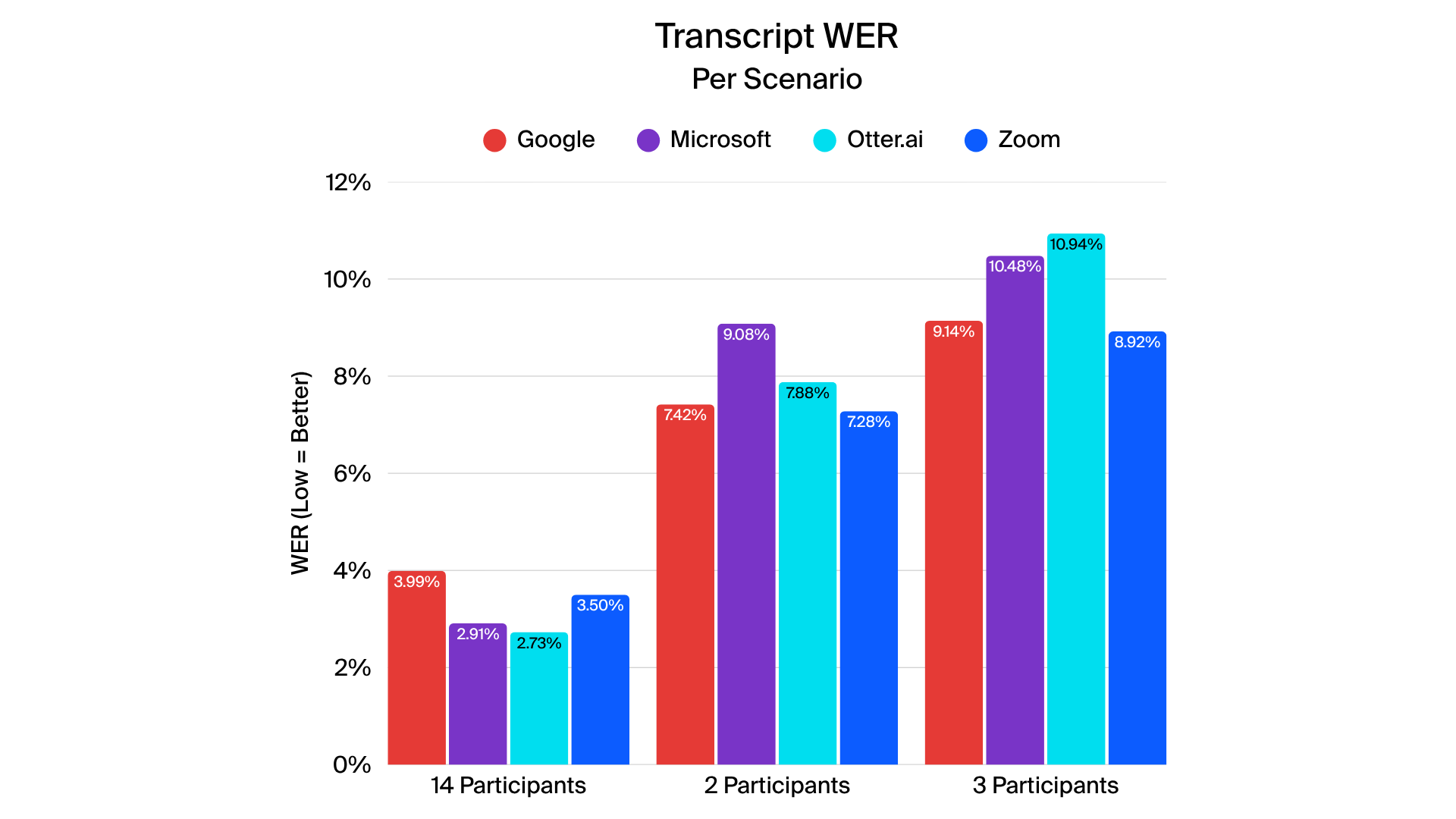
Transcription performance varied depending on meeting complexity, speaker accents, and background conditions. For this report, the tested transcripts represent the full meeting transcript generated after a meeting recording (sometimes referred to as the offline transcript). The evaluation focuses on each vendor’s ability to accurately convert speech to text using automated speech recognition (ASR). Zoom’s performance in this context reflects its transcription capabilities as applied to meeting recordings.
Zoom generally produced low overall word error rates, performing particularly well in scenarios with multiple speakers and technical content, though results were more varied in certain complex meetings, such as larger 14-participant calls. Rare word detection was a distinguishing factor, where Zoom outperformed other providers, demonstrating higher accuracy for specialized terminology.
Closed captions
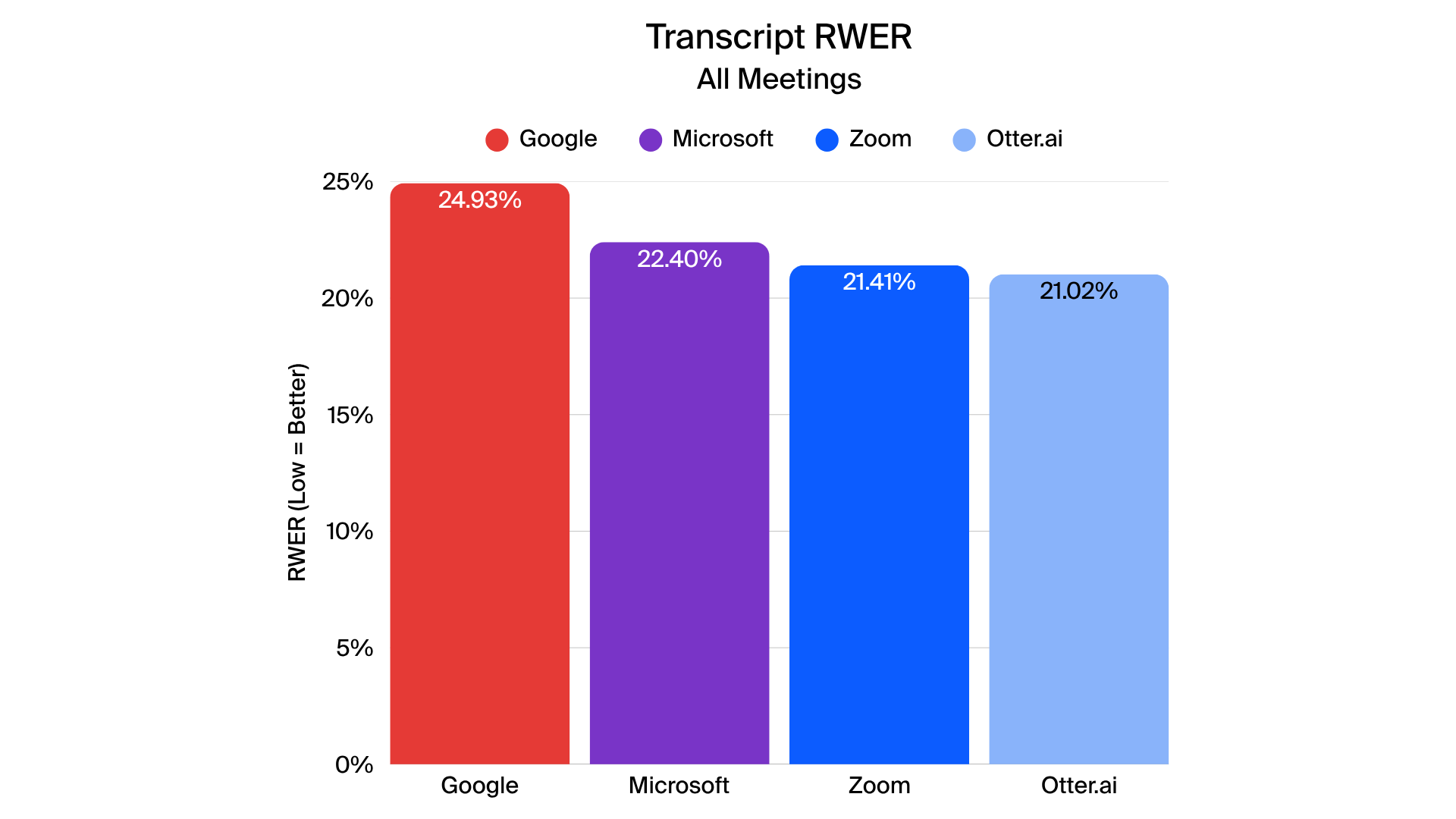
In closed-caption testing, Zoom delivered more accurate and stable captions across all four tested languages. Metrics such as normalized WER (N-WER) and rare word WER (R-WER) were generally lower for Zoom, indicating fewer errors across most scenarios. Zoom also generated fewer revisions during live captions, creating a smoother and more coherent experience for viewers.
Translated closed captions
When evaluating translated captions, Zoom demonstrated leading performance across English-to-French, English-to-Spanish, and English-to-Japanese translations. MetricX scores indicate high translation fidelity, reflecting accurate context, grammar, and terminology. Other providers showed varying levels of translation consistency, particularly in complex or rapid speech scenarios.
Meeting summaries
Zoom’s meeting summaries achieved high marks in completeness, clarity, and coverage of action items, closely approaching the top provider in overall summary quality. Microsoft maintained slightly higher scores in overall summary comprehensiveness, while Zoom performed particularly well in capturing key points and minimizing hallucinations in certain scenarios. Google and Otter.ai showed particular challenges in entity recognition and action item detection. Only summaries in English were tested.
These detailed results illustrate how each provider’s AI capabilities performed across varied real-world scenarios. Zoom’s consistent performance across multiple metrics highlights its competitive strength in transcription, captioning, translation, and summary generation.
AI continues to advance rapidly, shaping how communication platforms support collaboration and productivity. The evaluation by TestDevLab demonstrates that Zoom maintains a strong position in AI-enabled features, offering accurate transcription, reliable closed captions, and robust translation capabilities across multiple languages. While other providers show strengths in specific areas, Zoom’s combination of lower error rates, stable captions, and higher translation quality supports clear communication, and accurate understanding.
These results highlight the growing role of AI tools in streamlining meeting workflows, enhancing accessibility, and enabling teams to focus on strategic tasks rather than administrative overhead. As AI evolves, ongoing testing will be critical to understanding how different platforms meet the demands of increasingly diverse and complex communication scenarios.